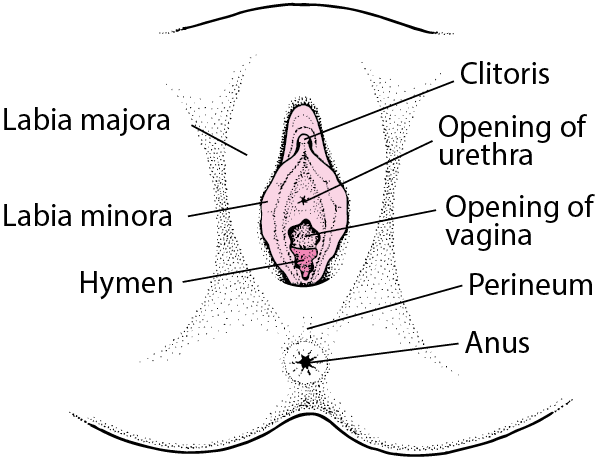
This summary addresses squamous cell cancer of the vulva and vulvar intraepithelial neoplasias (VIN), some of which are thought to be precursors to invasive squamous cell cancers. The labia majora are the most common sites of vulvar carcinoma and account for about 50% of cases. The labia minora account for 15% to 20% of vulvar carcinoma cases.
Vulvar Cancer – Women’s Health Issues – MSD Manual Consumer Version
Aug 29, 20221. Introduction. According to the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Database, vulvar cancer accounts for 4% of all female genital tract cancers, and is considered as a rare gynecologic malignancy [].The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), estimates that approximately 45,000 new cases of vulvar cancer are diagnosed each year, of which 50.1% are in high-income

Source Image: jpgo.org
Download Image
Diagnosing vulvar cancer. Tests and procedures used to diagnose vulvar cancer include: Examining your vulva. Your doctor will likely conduct a physical exam of your vulva to look for abnormalities. Using a special magnifying device to examine your vulva. During a colposcopy exam, your doctor uses a device that works like a magnifying glass to
Source Image: mater.ie
Download Image
Vulvar field resection based on ontogenetic cancer field theory for surgical treatment of vulvar carcinoma: a single-centre, single-group, prospective trial – The Lancet Oncology Cancer of the vulva accounts for 4.7% of malignant neoplasms in the genital tract. It is the fourth most frequent gynecologic cancer.1 … For carcinoma in situ (also classified as VIN III) of the vulva, the full thickness of epithelium usually is abnormal. It often is difficult to distinguish between benign squamous hyperplasia and

Source Image: facebook.com
Download Image
Vulvar Cancer In Situ Can Also Be Documented As
Cancer of the vulva accounts for 4.7% of malignant neoplasms in the genital tract. It is the fourth most frequent gynecologic cancer.1 … For carcinoma in situ (also classified as VIN III) of the vulva, the full thickness of epithelium usually is abnormal. It often is difficult to distinguish between benign squamous hyperplasia and It has been estimated that ~6120 new cases of vulvar cancer will … B. et al. Molecular characterization of invasive and in situ squamous neoplasia of the vulva and implications for morphologic
Ghamriny’s Clinical Dermatology
Pelvic exam: An exam of the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and rectum.A speculum is inserted into the vagina and the doctor or nurse looks at the vagina and cervix for signs of disease. A Pap test of the cervix is usually done. The doctor or nurse also inserts one or two lubricated, gloved fingers of one hand into the vagina and places the other hand over the lower abdomen Cancer of the vulva – Hacker – 2015 – International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics – Wiley Online Library

Source Image: obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Download Image
Journal of Postgraduate Gynecology & Obstetrics: October 2018 Pelvic exam: An exam of the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and rectum.A speculum is inserted into the vagina and the doctor or nurse looks at the vagina and cervix for signs of disease. A Pap test of the cervix is usually done. The doctor or nurse also inserts one or two lubricated, gloved fingers of one hand into the vagina and places the other hand over the lower abdomen

Source Image: jpgo.org
Download Image
Vulvar Cancer – Women’s Health Issues – MSD Manual Consumer Version This summary addresses squamous cell cancer of the vulva and vulvar intraepithelial neoplasias (VIN), some of which are thought to be precursors to invasive squamous cell cancers. The labia majora are the most common sites of vulvar carcinoma and account for about 50% of cases. The labia minora account for 15% to 20% of vulvar carcinoma cases.
Source Image: msdmanuals.com
Download Image
Vulvar field resection based on ontogenetic cancer field theory for surgical treatment of vulvar carcinoma: a single-centre, single-group, prospective trial – The Lancet Oncology Diagnosing vulvar cancer. Tests and procedures used to diagnose vulvar cancer include: Examining your vulva. Your doctor will likely conduct a physical exam of your vulva to look for abnormalities. Using a special magnifying device to examine your vulva. During a colposcopy exam, your doctor uses a device that works like a magnifying glass to

Source Image: thelancet.com
Download Image
What are the effects of gynaecologic cancer on women? – Quora Jul 5, 2023But cancer can form anywhere on your vulva. Vulvar cancer symptoms include: Color changes, including skin that looks darker or lighter than usual, or patches of white skin. Thickened or rough skin patches. Growths, including lumps, wart-like bumps or ulcers that don’t heal. Itching or burning that doesn’t improve.

Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Journal of Postgraduate Gynecology & Obstetrics: May 2017 Cancer of the vulva accounts for 4.7% of malignant neoplasms in the genital tract. It is the fourth most frequent gynecologic cancer.1 … For carcinoma in situ (also classified as VIN III) of the vulva, the full thickness of epithelium usually is abnormal. It often is difficult to distinguish between benign squamous hyperplasia and
Source Image: jpgo.org
Download Image
Vulvar field resection: Novel approach to the surgical treatment of vulvar cancer based on ontogenetic anatomy – ScienceDirect It has been estimated that ~6120 new cases of vulvar cancer will … B. et al. Molecular characterization of invasive and in situ squamous neoplasia of the vulva and implications for morphologic

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Journal of Postgraduate Gynecology & Obstetrics: October 2018
Vulvar field resection: Novel approach to the surgical treatment of vulvar cancer based on ontogenetic anatomy – ScienceDirect Aug 29, 20221. Introduction. According to the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Database, vulvar cancer accounts for 4% of all female genital tract cancers, and is considered as a rare gynecologic malignancy [].The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), estimates that approximately 45,000 new cases of vulvar cancer are diagnosed each year, of which 50.1% are in high-income
Vulvar field resection based on ontogenetic cancer field theory for surgical treatment of vulvar carcinoma: a single-centre, single-group, prospective trial – The Lancet Oncology Journal of Postgraduate Gynecology & Obstetrics: May 2017 Jul 5, 2023But cancer can form anywhere on your vulva. Vulvar cancer symptoms include: Color changes, including skin that looks darker or lighter than usual, or patches of white skin. Thickened or rough skin patches. Growths, including lumps, wart-like bumps or ulcers that don’t heal. Itching or burning that doesn’t improve.